IT hiccups happen when you least expect them. One fine Friday morning, emails freeze and the following day, a server crashes. Employees struggle with workarounds, and productivity hits rock bottom.
What’s even worse?
Clients notice fast, and complaints start rolling in.
Not every company has a large IT team. Hiring experts for every niche — cloud, security, networks — all of it, costs a lot. That’s when managed IT steps in to handle the mess.
Managed service providers help businesses manage and optimize their IT environments, whether on-premises, in the cloud, or across hybrid setups. They also watch for signs of trouble early on and step in before problems disrupt work. This take-charge approach lets IT achieve its business goals, instead of going back to the drawing board time and again. What’s required here?
- Link on-premises systems with cloud for smoother growth.
- Spot potential issues early on with continuous monitoring before they become noticeable.
- Keep IT aligned with the core business needs.
- Allow in-house teams to focus on important projects instead of wasting time in firefighting tech issues.
According to Forbes, “The global managed services market is projected to grow from $330.37 billion in 2025 to $878.71 billion by 2032.”
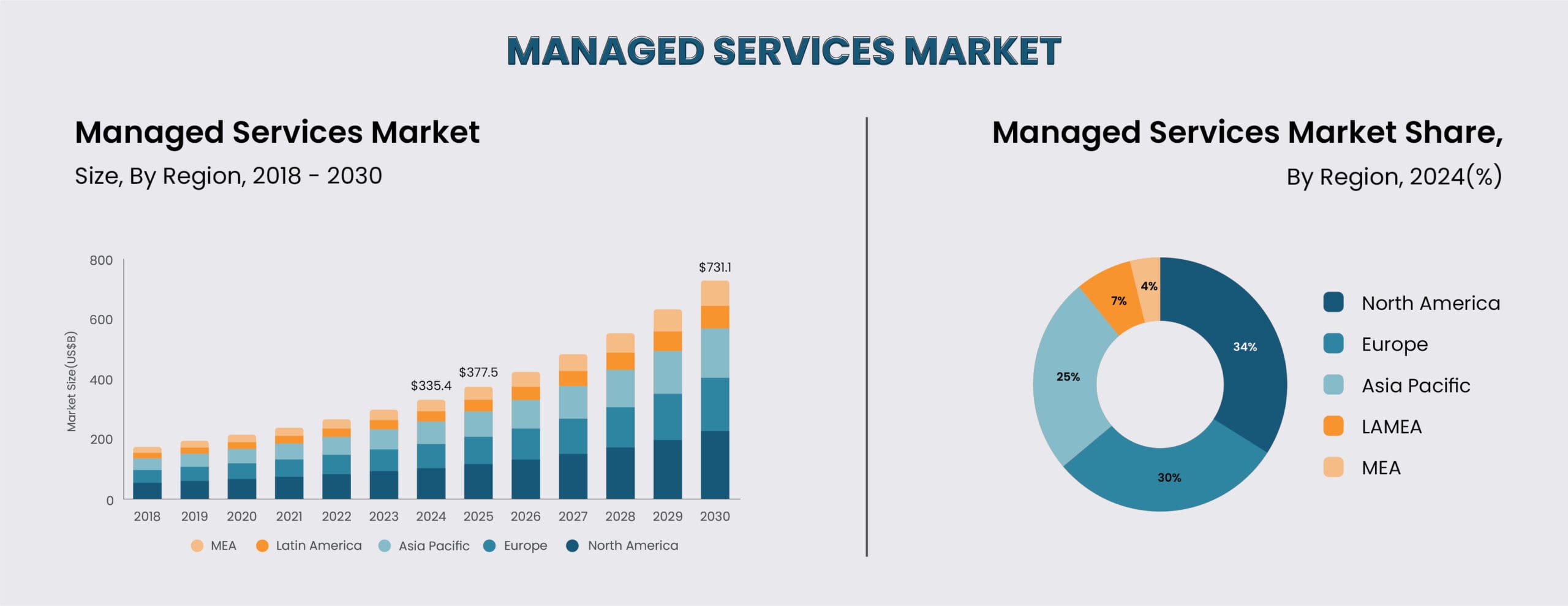
Spending is rising. Companies aren’t just looking to cut corners on IT expenses; they want IT that keeps running and can handle growth without constant firefighting.
This guide explains the mechanics of managed IT services, their benefits, and the range of service models available. It also weighs the challenges, while using practical examples to substantiate why adoption is accelerating across organizations of all sizes.
What Are Managed IT Services?
Managed IT services are when a company hires another company to handle parts of its IT. This isn’t just fixing things when they break. It’s watching systems all the time to stop problems before they happen.
Imagine a small business with five servers. Without monitoring, one server fails, files get lost, employees sit idle, and revenue takes a hit. With managed services, someone is watching the systems. They notice problems early, apply updates, take backups, and step in quickly before things get worse.
Providers usually sign contracts that clearly mention what they manage, how fast they would respond, and reporting schedules. This helps smaller teams gain access to expertise they would not afford otherwise. Larger teams save time and avoid constant firefighting.
6 Core Benefits of Managed IT Services

Managed IT services offer a myriad of business benefits and a few of them are listed below.
1. Predictable Costs
IT surprises are expensive. Fixing broken hardware or emergency software patches can eat into budgets. Managed services often come with a flat monthly fee.
2. Access to Experts
Technology changes fast. Security threats evolve. Networks expand. Managed service providers have niche experts for core areas such as cloud computing, networking, and cybersecurity to name a few. Small teams get expert support without hiring in-house employees.
3. Flexibility to Scale
Businesses grow, and teams need to expand. Managed services scale too. Adding new users or locations doesn’t mean buying a server today and another next year. The provider adjusts resources.
4. Reliable Systems
Downtime frustrates employees and customers. Providers monitor systems constantly. Problems are fixed before anyone notices. Work flows more smoothly.
5. Security and Compliance
Hackers barely take a break and keep enterprises on their toes. MSPs keep a constant watch over networks. They protect endpoints across the enterprise and respond the moment threats surface. What’s more? They also help enterprises achieve GDPR and HIPAA compliance by making regulatory demands less of a problem and more of a structured practice.
6. Focus on Core Work
When routine IT tasks are handled externally, employees can focus on high-value projects that matter, which involve improving products, serving customers, or growing the business.
Some IT resellers use White label MSP Services. They sell managed IT solutions under their brand. The provider handles technical work behind the scenes. This expands offerings without building a full IT team.
Common Types of Managed IT Services
Managed IT services can cover different areas, depending on needs.
Infrastructure Monitoring and Management
Providers watch servers, storage, and networks. They fix small issues before they become big problems.
Cloud Services
Many companies use cloud apps and storage. Providers manage accounts, migration, and maintenance. Employees access systems without worrying about setup or downtime.
Cybersecurity Services
Skipping cybersecurity isn’t an option anymore. In 2024 alone, the avg. data breaches in the U.S. cost around USD 9.36 million. That reality makes proactive security through managed IT services not a budget line but a business safeguard.
Compliance Support
Compliance Support Some industries cannot afford to overlook rules and regulations. Managed IT providers assist with creating policies, preparing audit material, and keeping the right records in place so that standards are met and businesses stay out of regulatory trouble.
Backup and Disaster Recovery Support
Data loss can be purely accidental or a result of a major failure. Having the right provider helps you back up your invaluable data and test recovery plans regularly.
Help Desk Support
Employees get support for software or hardware issues. Providers respond quickly so work isn’t stalled.
Network and Connectivity Management
Providers manage routers, switches, and internet connections. Offices and remote teams stay connected without interruptions.
Limitations of Managed IT Services
Managed services are useful, but they have limitations.
1. Vendor Dependence
Outsourcing means relying on another company. Contracts and clear communication are essential.
2. Extra Costs
Some contracts don’t cover emergencies or special projects. Companies must read agreements carefully.
3. Limited Customization
Standard service packages may not suit unique business needs. Custom arrangements may be needed.
4. Skills Gap
Relying too much on external teams can reduce internal knowledge. Maintaining basic IT understanding is important.
5. Communication
External teams may misunderstand priorities. Clear contact points and regular updates are critical.
3 Key Steps When Choosing an Managed IT Service Provider
The choice of your MSP will shape how your IT runs and how your business grows. Look for one that fits now and can keep pace as things expand.
Evaluate your existing IT environment
First things first! Take a hard look at your setup. Note what’s solid. Spot the workloads that eat up resources. Call out the weak spots that slow you down. This review should clearly tie back to your enterprise’s goals. A company looking for supplemental support to assist an internal IT team has very different requirements as opposed to one that needs a fully managed solution.
Ask for a system audit
Once you have shortlisted a few providers, get an audit done. This exercise shows you whether or not the MSP understands your technology landscape. It will also help you gain more confidence in their tool management, platforms, and compliance standards. A provider that struggles here will likely fall short once operations begin.
Evaluate flexibility and scalability
An MSP should have more capacity than you need today. Otherwise, sooner or later, they will turn into a constraint rather than an enabler.
If your provider can’t keep up with extra hours, cloud changes, or more employees, your business will feel it. Scaling matters.
Managed IT Services Tools for MSPs
Managed IT services providers leverage the following tools to maximize efficiency:
- RMM or Remote Monitoring : Tracks systems & sends alerts before small or big problems start hampering operations.
- Professional Services Automation (PSA): Manages tickets, workflow, and staff allocation.
- Backup & Recovery Tools: Safeguard and restore data quickly.
- Analytics & Reporting Tools: Log system health and major risks
- Identity & Access Management (IAM / SSO): One place to control logins. If someone leaves the team, you cut them off here.
- Patch & Update Management: Updates are boring, but missing one is how hacks happen. This just pushes them out on time.
- Network & Performance Monitoring: Like keeping an eye on blood pressure — if the network slows or drops, you know right away.
- SIEM / Log Management: Every click leaves a trail. These tools collect it and throw up a flag when something looks off.
- Mobile Device & Endpoint Management (MDM / EDR): A stolen laptop or phone shouldn’t mean stolen data. This locks them down.
- Security Tools: Managing firewalls, antivirus, and intrusion detection.
Conclusion
Companies deal with IT setbacks almost daily — a failed update, a slow network, or a security gap that puts data at risk. Managed IT Services step in to keep systems steady, protect information, and give access to skills that aren’t always available in-house. With a reliable partner handling the background work, staff can stay focused on projects that push the business forward.
Small or large teams gain a steady framework, reducing stress, improving efficiency, and providing a foundation for growth and long-term business success.




